Bushings are very important component
of Transmission system. These are used of providing insulation to equipment.
There are various types of
bushings available in the market, bushings are classified according to
following:-
(i)
Type of insulating material used
(ii)
Type of construction
(iii)
Insulation inside bushing
Let’s discuss about the same:-
(i)
Type of Insulating Material
Used:-
This classification depends
primarily on the application of the bushing, i.e. the purpose for which bushing
is used. These can be further classified as:-
(a)
Air-to-oil bushing
In this type of bushing there is
air is used as insulation at one end on bushing and oil acts as insulation at
other end. In these bushings oil end is approximately half as long as air end
as oil dielectric strength is more than two times than air at atmospheric
pressure.
(b)
Air-to-air
bushing
In This type of bushing air acts as insulation at both ends and is
used for applications where at end is open to atmospheric conditions and other
is at indoor conditions.
(c)
Air-to-SF6
bushings
This type of bushing is used for
SF6 insulated circuit breakers.
(d)
SF6-to-oil
bushings
This type of bushing is used as
shift from SF6 bus ducts and oil filled equipment.
(e)
Oil-to-oil
bushings
This type of bushing as
transition between Oil bus ducts and oil filled equipment.
(ii)
Type of
Construction:-
There are two types of bushings
depending upon type of construction, these are classified as below:-
(a) Solid
Type bushings also known as Bulk type bushings
(b) Capacitance
graded bushings also known as Condenser type bushings
Let’s discuss about these:-
(a)
Solid Type bushings:-
The kind of bushing, is normally
made with a focal conductor and porcelain or epoxy covers at either end and is
utilized essentially at the lower voltages through 25 kV. These bushings are generally utilized as a
part of utilizations extending from little distribution transformers and
circuit switchgears to vast generator venture up transformers and
hydrogen-cooled control generators.
The essential impediment of the
strong bushing is its capacity to withstand 60-Hz voltages over 90 kV.
Henceforth, its applications are restricted to 25-kV hardware appraisals, which
have test voltages of 70 kV. Late applications require low halfway release
confines on the 25-kV terminals amid transformer test and have brought about
additional limitations on the utilization of this sort of bushing.
In these cases, either an
extraordinarily outlined strong bushing, with one of a kind evaluating
protecting that empowers low innate halfway release levels, or a more costly
capacitance-reviewed bushing must be utilized.
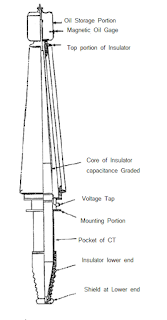
(b)
Capacitance
Graded Bushings:-
These bushings are utilized for
basically all voltage evaluations over 25-kV voltage and has been utilized for
bushings upto 1500-kV voltage.
These bushings utilizes directing
layers at foreordained spiral interims inside oil-impregnated paper or some
other protection material that is situated in the space between the focal
conductor and the protector.
Diverse makers have utilized an
assortment of materials and techniques for making capacitance-evaluated
bushings. Early techniques were to embed concentric porcelain barrels with
metallized surfaces or overlaid pressboard tubes with installed conductive
layers. Later outlines utilized conductive foils, commonly aluminum or copper,
in oil-impregnated kraft paper.
An elective strategy is to print
semiconductive ink (distinctive producers have utilized diverse conductivities)
on all or a portion of the oil-impregnated kraft-paper wraps.
The primary components are the
focal round conductor, onto which the capacitance-evaluated center is wound;
the best and lower protectors; the mounting rib; the oil and an oil-extension
top; and the best and base terminals.
Capacitance-reviewed bushings
include numerous more specialized and assembling subtle elements than strong
bushings and are hence more costly. These points of interest incorporate the
protection/directing layer framework, gear to wind the capacitor center, and the
oil to impregnate the paper protection.
In any case, it ought to be
noticed that the outspread measurement required for the capacitance-evaluated
bushing is considerably less than the strong development, and this saves money
on material inside the bushing also in the mechanical assembly in which the
bushing is utilized. Likewise, from a down to earth stance, higher-voltage
bushings couldn't in any way, shape or form be fabricated with a strong
development.
(iii)
Type of
Insulation inside Bushing
Still another order identifies
with the protecting material utilized inside the bushing. As a rule, these
materials can be utilized as a part of either the strong or
capacitance-evaluated development, and in a few sorts, more than one of these
protecting materials can be utilized as a part of conjunction. The accompanying
content gives a short portrayal of these sorts:
1. Air-Insulated Bushings
Air-protected bushings for the
most part are utilized just with air-protected mechanical assembly and are of
the strong development that utilizes air at air weight between the conductor
and the protectors.
2. Oil-Insulated or Oil-Filled Bushings
Oil-protected or oil-filled
bushings have electrical-review mineral oil between the transmitter and the
encasings in strong sort bushings. This oil can be contained inside the
bushing, or it can be imparted to the contraption in which the bushing is
utilized. Capacitance-reviewed bushings likewise utilize mineral oil, typically
contained inside the bushing, between the protecting material and the
protectors for the motivations behind impregnating the kraft paper and
exchanging heat from the directing lead.
3. Oil-Impregnated Paper-Insulated Bushings
Oil-impregnated paper-protected
bushings utilize the dielectric cooperative energy of mineral oil and electric
evaluations of kraft paper to deliver a composite material with predominant
dielectric-withstand attributes. This material has been utilized broadly as the
protecting material in capacitance-evaluated centers for approximately the most
recent 50 years.
4. Gum Bonded or - Impregnated Paper-Insulated Bushings
Gum fortified paper-protected
bushings utilize a sap covered kraft paper to manufacture the
capacitance-reviewed center, while gum impregnated paper-protected bushings
utilize papers impregnated with tar, which are then used to create the
capacitance-evaluated center. The last kind of bushing has prevalent dielectric
attributes, equivalent with oil-impregnated paper-protected bushings.
5. Cast-Insulation Bushings
Cast-protection bushings are
developed of a strong thrown material with or without an inorganic filler.
These bushings can be both of the strong or capacitance-evaluated types,
despite the fact that the previous sort is more illustrative of present
innovation.
6. Gas-Insulated Bushings
Gas-protected bushings utilize
pressurized gas, for example, SF6 gas, to protect between the focal conductor
and the rib. It utilizes the same pressurized gas as the electrical switch, has
no capacitance reviewing, and utilizes the measurements and situation of the
ground shield to control the electric fields.
Bushing rating and mounting are
depended upon type of interface. HT
Bushing above 1000 V are designed as per IS 2099
There are 5 types of interfaces:-
1. Interface
A1
2. Interface
B1 & B2
3. Interface
C1 & C2
4. Interface
D1 & D2
5. Interface
F1, F2 & F3
Short circuit ratings of all
above mentioned bushings is as below:-
|
Interface Type
|
Contact Type
|
Current Rating(A)
|
RMS(kA)
|
Peak asymmetrical current rating kA
|
||
|
1 Sec
|
2 Sec
|
3 Sec
|
||||
|
A1
|
Pin and Socket
|
250
|
12.5
|
9.0
|
7.5
|
31
|
|
B1
|
Pin and Socket
|
250
|
12.5
|
9.0
|
7.5
|
31
|
|
B2
|
Pin and Socket
|
400
|
16.0
|
11.3
|
9.2
|
40
|
|
C1
|
Bolted
|
630
|
28.0
|
19.7
|
16.1
|
70
|
|
C2
|
Bolted
|
1250
|
75.0
|
53.0
|
43.3
|
>150
|
|
D1
|
Bolted
|
800
|
50.0
|
35.3
|
28.8
|
125
|
|
D2
|
Bolted
|
1250
|
75.0
|
53.0
|
43.3
|
>150
|
|
F1
|
Bolted
|
2500
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|
F2
|
Bolted
|
630
|
28.0
|
19.7
|
16.1
|
70
|
|
F3
|
Bolted
|
1250
|
75.0
|
53.0
|
43.3
|
>150
|
Applications of different types
of bushings:-
A1 Interface type bushings :-
These types of bushings are
useful for equipment insulated with oil fluids such as Transformers,
Switchgear, Capacitors. There are
following types of A1 interface type bushings:-
(i) 180AR-1
(i) 180AR-1
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 222 X 106 (height X Breadth)
(ii) K180AR-1
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 222 X 106 (height X Breadth)
(iii) 180AR-2
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 284 X 168 (height X Breadth)
(iv) K180AR-2
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 284 X 168 (height X Breadth)
(v) 180AR-3
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 171 X 55 (height X Breadth)
(vi) K180AR-3
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current
Rating- 250A, Dimensions are- 171 X 55 (height X Breadth)
There is another interface A1
bushing known as In-Air bushing for dry type transformers, Motors , Switchgear
and capacitors.
Types of Bushings are
(i)
180A-24P-O
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current Rating- 250A, Creepage
Distance (mm)- 630 mm
(ii)
180A-24P-O
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 250A, Creepage
Distance (mm)- 630 mm
Interface B Type Bushings:-
This is useful for Oil fluids
such as Transformer, Switchgear & Capacitors.
There are following types of
bushings:-
(i)
400T1
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(ii)
K400T1
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(iii)
M400T1
Voltage Rating- 36 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(iv)
400AR-1
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(v)
K400AR-1
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(vi)
M400AR-1
Voltage Rating- 36 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(vii)
400AR-2
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(viii)
K400AR-2
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(ix)
M400AR-2
Voltage Rating- 36 KV, Current Rating- 400A
(x)
400AR-8
Voltage Rating- 12 KV, Current Rating- 250A
(xi)
K400AR-8
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 250A
(xii)
M400AR-8
Voltage Rating- 24 KV, Current Rating- 250A
There is another type of
Interface B type switch is specifically used for SF6 circuit breakers.
Similarly there are other
Interface type bushings and have same applications only difference is in their
mounting designs , voltage rating and current rating.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.